Much has been written about 5G technology – some of it factual, some of it “fake news”. Depending on who you ask, the advent of 5G technology will either revolutionise the way both individuals and businesses interact with the digital world or be humankind’s downfall. In our latest knowledge leadership piece, we take a deeper look at 5G technology: what is really is, where it is heading and what businesses can do to prepare for it.
What is 5G technology?
When 5G technology was in its infancy (back in 2015!), the 5G Innovation Centre (5GIC) at the University of Surrey described it as “the next generation of mobile connectivity technologies that supports mobile broadband as well as networking of billions of devices.”
As the technology, and the R&D work driving it, has matured so has the definition of what 5G technology is. In 2020, the ITU (the International Telecommunication Union, the United Nations specialised agency for information and communication technologies) described 5G as a set of mobile networks and services that “connects people, things, data, applications, transport systems and cities in smart networked communication environments. The networks transport a huge amount of data much faster, reliably connect an extremely large number of devices and process very high volumes of data with minimal delay”.
The ITU plays a key international role in the management of the radio spectrum that underpins these mobile networks and has developed a set of globally applicable standards for what constitutes a 5G technology. This is known as the IMT-2020 standards.
At the point of writing, there are four mobile technologies that are approved as meeting the stringent IMT-2020 performance specifications.
The first two, 3GPP 5G-SRIT and 3GPP 5G-RIT, were developed by the Third Generation Partnership Project. The third, 5Gi, was provided by the Telecommunications Standards Development Society India. It is an updated version of 3GPP 5G-RIT and has been designed mainly to improve rural coverage.
It was announced in February 2022, that a fourth technology, DECT 5G-SRIT, has met the IMT-2020 standards and been added as an acknowledged 5G technology. This technology, which is a non-cellular, autonomous and decentralised in nature, “supports a range of uses, from wireless telephony and audio streaming to industrial Internet of Things (IoT) applications, particularly in smart cities”.
The benefits of 5G technology
Adoption of 5G technology will bring a range of exciting benefits for both consumers and businesses. These include:
- Faster connection speeds – this is the most widely known benefit of 5G technology. Theoretically, 4G has a maximum speed of about 100MB per second but that is under perfect laboratory conditions. In contrast, 5G has the potential to reach 10GB per second.
- Increased reliability – in addition to increased speed, 5G technology will also deliver more reliability and less data loss for consumers and businesses using business applications.
- Decreased latency – latency is the gap between when the data is sent and when it is received. When you have high latency, there will be a noticeable lag in things like response times. 5G technology has the ability to improve the latency rates which will be very helpful for businesses who are looking to get involved with IoT devices.
- Higher device capacity –mobile networks are not unlimited and can only handle a certain amount of devices and data transmissions simultaneously. As businesses use more devices and therefore transfer more and more data, the 4G network is not always able to handle these increases. 5G, in contrast, will be able to. Vodafone estimates that “5G is expected to support up to 1 million connected devices per 1 square kilometre, compared to around 2,000 connected devices per 1 square kilometre with 4G”.
Challenges of adopting 5G technology
As with all technologies, 5G technology does have its challenges. These include:
- Cost – 5G technology is still very expensive.
- Integration with legacy technology – In addition, the devices that currently support 5G are limited. At the moment, many IoT devices use LTE (LTE stands for Long Term Evolution, a term used for the particular type of 4G that delivers a fast mobile Internet experience). Many businesses will continue to use LTE devices even once 5G IoT devices become more prevalent. It is therefore very important that these two different types of IoT technology are able to integrate with each other.
- Security risks – Network security is a major challenge to widespread 5G technology adoption. Much of 5G’s wireless telecommunications infrastructure is built on legacy technologies, such as 4G LTE networks. This means that any vulnerabilities that already exist in those networks will threaten the security of 5G networks. In addition, there are security risks attached to both the technology infrastructure that the network uses (for example cellular towers or small cells mounted on a building or a tree) as well as the cellular devices themselves. Both are at risk of attack, either physically or digitally.
- Scarcity of radio spectrum – Like previous mobile generations, 5G technology uses the radio spectrum to send data between masts and mobile devices. At the time of writing, 5G technology uses the 3.4GHz band, the 3.6-4GHz band, and the 700MHz band are being used in the UK. As 5G technologies develop, finding additional radio spectrum may prove to be a challenge, particularly for businesses looking to develop their own private 5G networks for applications such as a smart factories or machine to machine communications for industry automation.
5G for businesses
While 5G technology has a wide range of consumer-focused uses, such as smart homes, smart cities and autonomous cars, there are also many uses of 5G for businesses. These include:
- Virtual or augmented reality – Augmented and virtual reality are two technologies that would benefit significantly from 5G integration. 5G-enabled AR and VR have the potential for uses in multiple industries, including manufacturing, gaming, media, automotive and healthcare.
- Smart factories – Gartner defines a smart factory as “a concept used to describe the application of different combinations of modern technologies to create a hyperflexible, self-adapting manufacturing capability.” 5G technology creates the possibility of faster operation as well as new capabilities and efficiencies in industrial processes.
- Machine to machine communications – Machine-type communication (MTC), or machine-to-machine communication (M2M), is anticipated to be one of the primary business applications delivered by 5G networks. MTC/M2M will be vital for the levels of industrial automation that will take place in future smart factories. In addition, there are a wide range of other M2M applications which will benefit from the network improvements delivered by 5G technology.
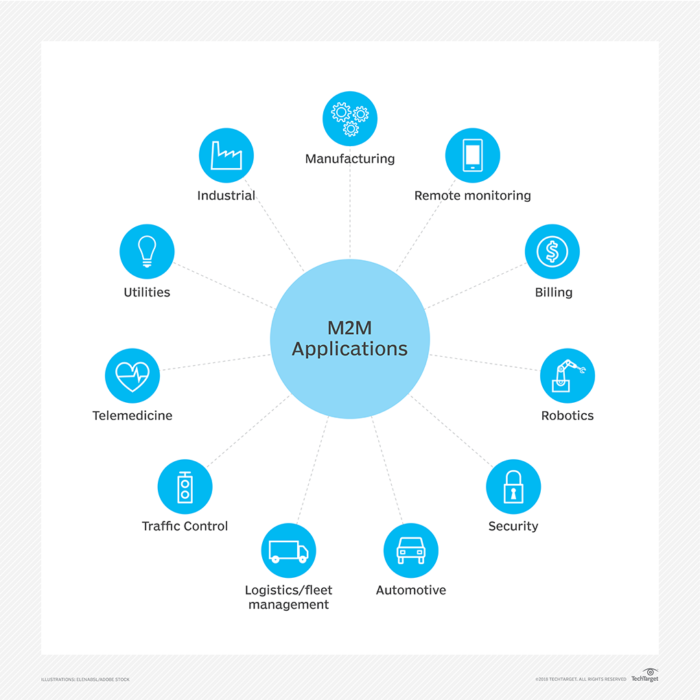
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/iotagenda/definition/machine-to-machine-M2M
What do businesses need to do to prepare for the 5G technology revolution?
- Invest: If businesses want to remain competitive when the full-scale 5G technology revolution kicks in, they will need to have 5G-ready equipment that is ready to go. Therefore, businesses must start including 5G investments in their budgets.
- Strategise: 5G technology, and its applications, is constantly evolving and getting better. If businesses want to get on board early, they need to start thinking today about how they are going to use 5G technology both now and in the future.
- Prepare: Businesses may want to use 5G technology to improve their AI, automation and IoT capabilities but they may not actually be ready, from a data point of view, to do so. Businesses who want to adopt 5G technology successfully need to have a plan for how they will collect, store and use the richer data that will come hand and hand with the 5G technology revolution.
- Educate: Most people in your business team will have heard of 5G, but they may not have a clear understanding of the uses of 5G for businesses. It is therefore important to educate team members on how 5G technology can, and eventually will, be used within your business.
How can TVision Technology help you?
To find out how using 5G technology and Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central could help your business, get in touch with one of our experienced TVision team.
