In today’s digital era, managing vast amounts of data efficiently is a paramount challenge for businesses. Azure Blob Storage, a component of Microsoft’s Azure cloud platform, emerges as a robust solution for storing and managing massive volumes of unstructured data. In this article, we take a deep dive into what Azure Blob Storage is, what its key features are and the advantages to making a move to this form of data storage.
What is Azure Blob Storage?
Azure Blob Storage is Microsoft’s object storage solution for the cloud and is optimised for storing massive amounts of unstructured data.
Blob (Binary Large Objects) Storage is designed for:
- Serving images or documents directly to a browser
- Storing files for distributed access
- Streaming video and audio
- Writing to log files
- Storing data for backup and restore, disaster recovery, and archiving
- Storing data for analysis by an on-premise or Azure-hosted service

It offers three types of resources as illustrated in the diagram below:
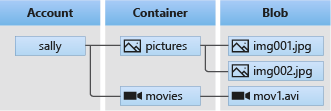
1. Storage account
A storage account provides a unique namespace in Azure for your data. Every object that you store has an address that includes your unique account name. The combination of the account name and the Blob Storage endpoint forms the base address for the objects in your storage account.
There are three different types of storage accounts in Azure Blob Storage:
- Generate-purposev2 – this is the standard storage account type for blobs, file shares, queues and tables.
- Block blob – this is a premium storage account type for block blobs and append blobs. This type is recommended for scenarios with high transaction rates or that use smaller object or require consistently low storage latency.
- Page blob – this is a premium storage account type for page blobs only.
2. Containers
A container organises a set of blobs, similar to a directory in a file system. A storage account can include an unlimited number of containers and a container can store an unlimited number of blobs.
3. Blobs
Azure Blob Storage supports three types of blobs:
- Block blobs that store text and binary data.
- Append blobs that are made of blocks like block data but are optimised for append operations.
- Page blobs store random access files up to 8TiB in size.
Why do Business Central users start using Azure Blob Storage?
For Business Central SaaS users, Microsoft provides each SaaS instance with 80 GB of database storage (plus 1-3GB of additional storage capacity based on the number of Business Central licences they have and what type of licence these are). This is intended to be more than enough storage space for users. However, sometimes this isn’t the case.
For Business Central On-premise users, the introduction of the Universal Code Initiative in October has meant that saving files on on-premise servers has becoming increasingly expensive.
For many Business Central users, Blob Storage become a more cost-effective way of storing and managing their unstructured data.
What considerations affect Azure Blob Storage costs?
There are a number of factors which affect the total cost for customers:
- Access Tiers – there are four access tiers in Azure Blob Storage, Hot/Cool/Cold/Archive. Cool tiers offer cheaper storage but more expensive read and write operations. Cool tiers are best suited for data storage while hot tiers are suited for integrations.
- Volume of data stored per month – as with most subscription services, data storage costs increase as the volumes increase. Current pricing details can be found at https://azure.microsoft.com/en-gb/pricing/details/storage/blobs/#pricing.
- Quantity and types of operations performed – costs are affected by the types of operations customers need to perform on their data. Write operations are generally more expensive than read operations.
- Data redundancy option selected – Azure Storage always stores multiple copies of your data so that it is protected from both planned and unplanned events. There are three basic levels of data redundancy:
- Locally redundant storage (LRS) which copies data synchronously three times within a single physical location in a primary region. This is the least expensive option.
- Zone-redundant storage (ZRS) which copies data synchronously across three Azure availability zones in the primary region.
- Geographically redundant storage (GRS) which copies data synchronously three times within a single physical location using LRS and then copies this data asynchronously to a single physical location in a secondary region.
For Business Central users to get an idea of how much Azure Blob Storage would cost for their business, a Pricing Calculator can be found at https://azure.microsoft.com/en-gb/pricing/calculator/.
What are the advantages of using Azure Blob Storage?
Businesses opt for Blob Storage for several compelling reasons:
1. Scalability and Flexibility
Azure Blob Storage offers unparalleled scalability, allowing businesses to seamlessly scale their storage needs as data requirements grow. Whether dealing with documents, images, videos, or other unstructured data, Azure Blob Storage accommodates diverse data types, providing the flexibility needed for modern applications.
2. Cost Efficiencies
With tiered storage options like Hot, Cool, and Archive tiers, Azure Blob Storage enables businesses to optimize costs based on data access patterns. Frequently accessed data can be stored in the Hot tier for quick retrieval, while less accessed or archival data can be moved to the more cost-effective Cool or Archive tiers.
3. Efficient Data Retrieval
Searching for specific data within large datasets can be a daunting task. Blob Storage introduces Blob Indexer, a powerful tool that enables efficient data retrieval based on metadata and content. This feature significantly enhances data discovery, making it easier for developers and users to locate and access the information they need.
4. Security and Compliance
Security is paramount in the cloud, and Azure Blob Storage addresses this concern comprehensively. With features such as Azure Active Directory integration, encryption at rest, and role-based access control, businesses can ensure that their data remains secure and compliant with industry
5. Integration with Azure Services
Azure Blob Storage seamlessly integrates with other Azure services, creating a comprehensive ecosystem for developers. From Azure Functions for serverless computing to Azure Logic Apps for workflow automation, the interoperability of Azure services amplifies the capabilities of applications leveraging Blob Storage.
6. High Availability and Disaster Recovery
Businesses prioritise data availability and resilience against disruptions. Blob Storage offers multi-region redundancy, enabling data replication across different geographic regions. This ensures high availability and contributes to a robust disaster recovery strategy.
7. Developer-Friendly
Developers appreciate Blob Storage for its ease of use and compatibility with various programming languages. The Blob Indexer, for example, facilitates efficient data retrieval based on metadata and content, streamlining the development process and enhancing overall application performance.
How can you move your data to Azure Blob Storage?
Data can be moved to Azure Blob Storage in a number of different ways. Details of the different data transfer solutions available and how to select the solution best for you can be found here.
How TVision can help you
If you are currently a Business Central user and are considering a move to Azure Blob Storage, please contact us for a free, confidential discussion on how best to proceed.
